Why do we need Data?
July 8, 2025
Explores the importance of data and information in decision making.

Why do we go through extensive efforts to collect, transform, load, store, and aalyze volumes of data? Startups and corporations employ teams of professionals who often specialize in niche functions within data analytics such as data architect, data analyst, or data scientist in order to provide maximum value of their respective function to the enterprise. There must exist a valid and profit driven reason to place such a premium on the function and impact of data. The reason is data provides answers in the form of information that is paramount to the resolution of real-world problems while contributing to the sustainability and growth of organizations.
Data Integrity
High integrity data is a purely objective form of facts not influenced by human subjectivity. What we mean by integrity in the context of data is that the predicate of a given piece of data can be relied on to be true which entails accuracy, exclusivity or non-duplication, and consistency. Accuracy gives reliability to the literal qualitative or quantitative value. Exclusivity indicates the values are not represented anywhere else in the working dataset. And consistency means that the values of each individual datum in the working dataset exist within the realm of possible phenomena.
Necessity of data in decision making
Whether making journal entries to a general ledger, recording a hospital's daily admissions and discharges, or predicting the extent of raw materials needed for a factory's anticipated production, data is central to facilitating correct decisions. Driving decisions according to conclusions drawn from data instills confidence of correctness - data are facts and decisions based on facts are likely to produce correct results. Data's role in providing answers to questions in a decision making process may be illustrated like the below.
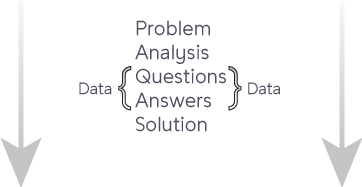
Data versus information
The words data and information are often used interchangeably. However, in the context of data analytics, data and information become terms denoting different things and should be treated with care by the practitioner. Data means raw objective facts such as rows stored in tables in a database or data warehouse and results in information usable by stakeholders to make insightful decisions. Information applies context and meaning to data ultimately leading to the fruits of data's labor. Summary statistics, graphs, charts, financial statements, and reports in general are examples of information that humans use to make decisions.
Summary
Using quality data to derive insights about organizations is imperative in an operational decision making process. Without data the ability to confidently stand on impactul decisions would be compromised and would inevitably lead to less than desirable outcomes. With the advent of big data and AI data that is effectively analysed and translated to meaningful business information data has never been more critical.
